Introduction When your vehicle needs repair or an upgrade, choosing the right replacement parts is crucial to its performance, safety, and longevity. One of the most debated topics among car owners, mechanics, and global auto parts buyers is whether to go with OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or aftermarket auto parts. Each option comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks depending on factors such as budget, vehicle make, intended use, and supplier reliability.
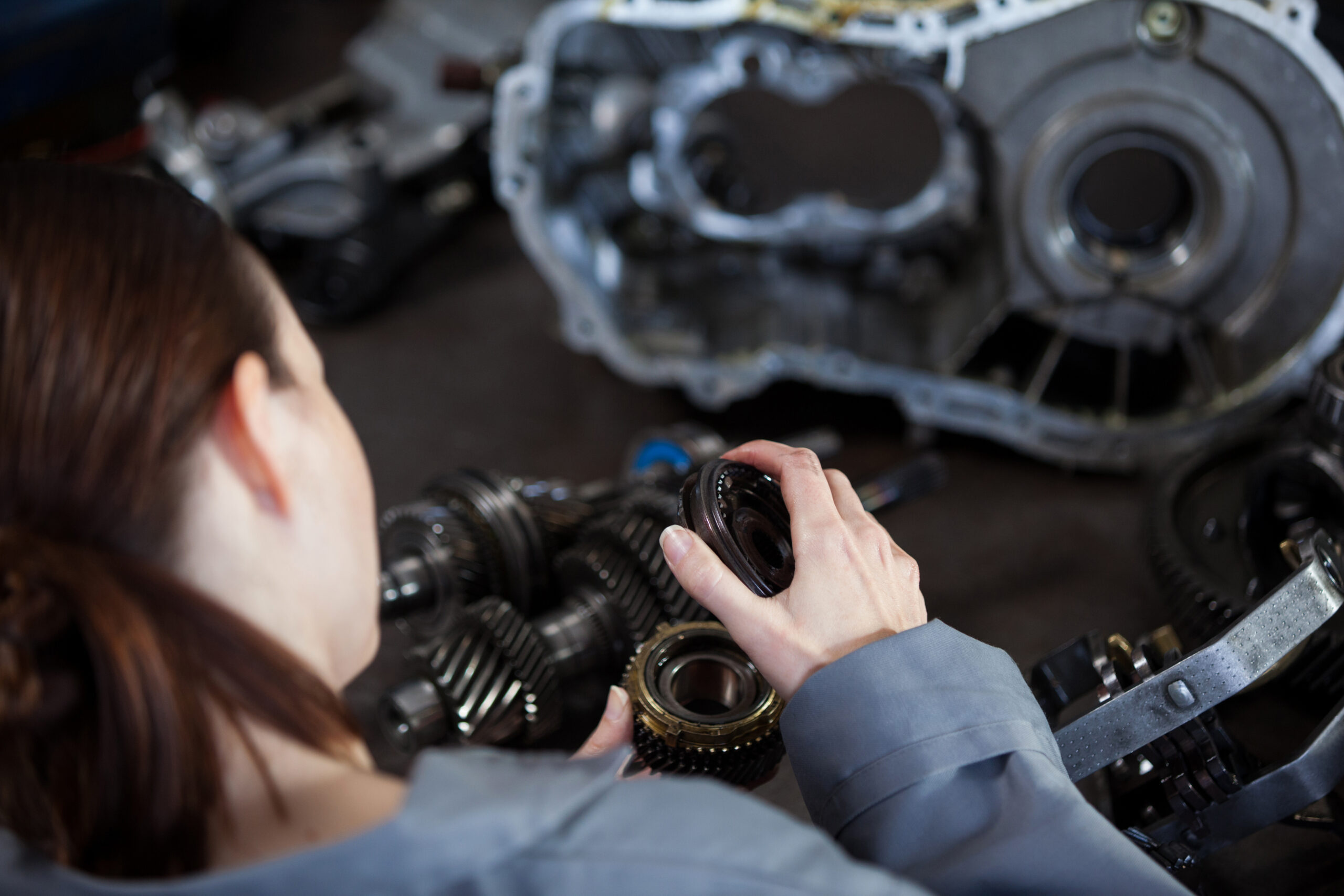
1. What Are OEM Auto Parts? OEM parts are manufactured by the same company that produced the original parts for your vehicle. These parts are often sold through dealerships or authorized distributors and are identical in fit, function, and material to the parts that originally came with your car.
- Advantages of OEM Parts:
- Guaranteed compatibility
- Reliable performance and durability
- Often backed by a manufacturer warranty
- Maintains resale value
- Disadvantages of OEM Parts:
- Higher cost
- Limited availability outside authorized channels
2. What Are Aftermarket Auto Parts? Aftermarket parts are made by third-party manufacturers. They are designed to function the same as OEM parts but may vary in quality, price, and material.
- Advantages of Aftermarket Parts:
- Cost-effective and widely available
- Greater variety and options for customization
- Some offer better performance than OEM parts
- Disadvantages of Aftermarket Parts:
- Quality varies greatly among brands
- Risk of incompatibility
- May void the manufacturer’s warranty if improperly installed
3. Use Cases for OEM vs. Aftermarket
- OEM:
- Luxury or newer vehicles where preserving originality matters
- Repairs under warranty
- Resale situations requiring documentation of genuine parts
- Aftermarket:
- Older vehicles where cost-saving is prioritized
- Performance upgrades (e.g., high-performance brake systems)
- DIY projects with flexible requirements
4. Tips for Purchasing Auto Parts Online
- Check part numbers against your vehicle’s VIN
- Verify seller reviews and business credibility
- Look for certifications (e.g., ISO, SAE compliance)
- Request photos, videos, and specifications before purchasing
- Confirm return/refund policy
Conclusion Both OEM and aftermarket auto parts serve a purpose in the automotive world. Understanding the key differences and evaluating your own vehicle’s needs and budget will help you make smarter decisions. Always work with trustworthy suppliers and don’t hesitate to ask for documentation or proof of quality.




Add comment